World Bank: Nigeria to Receive More Diaspora Remittances in 2024.
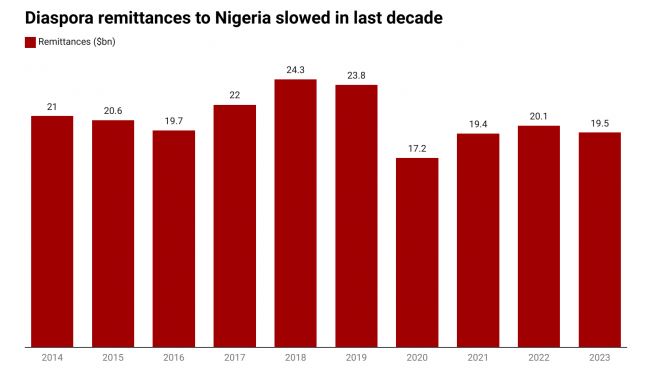
Nigeria has consistently been one of the top recipients of diaspora remittances, averaging about $20 billion annually over the last decade. These remittances have been a crucial source of foreign exchange, surpassing other foreign earnings for several countries. However, the growth in remittances has slowed recently, with a 3% drop recorded in 2023, bringing the total to $19.5 billion, according to the World Bank.
This decline is part of a broader trend affecting Low and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs), where remittance flows grew by just 0.77% between 2022 and 2023, compared to an 8.3% increase in the previous year. Despite this slowdown, the World Bank predicts a recovery, with remittance flows to LMICs expected to grow by 2.3% in 2024 and 2.8% in 2025.
In Nigeria, remittances play a vital role in supporting education, healthcare, infrastructure, and foreign exchange liquidity. To enhance this, the Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) has allowed international money transfer operators (IMTOs) access to the official foreign exchange market, a move aimed at increasing local currency liquidity. The CBN governor also revealed plans to double diaspora remittances, which currently contribute 6% of Nigeria’s GDP, in 2024.
The outlook for remittances in Nigeria is promising, with the potential for growth supported by strong labor markets in advanced economies, particularly the UK and the US, which are key sources of remittances. However, challenges such as high remittance costs, lack of competition, and potential global economic slowdowns remain. Additionally, external factors like geopolitical conflicts and climate risks could impact remittance flows in the coming years.
Share News with us via WhatsApp:08163658925 or Email: naijaeyes1@gmail.com
Join Our Social Media Channels:
WhatsApp: NaijaEyes
Facebook: NaijaEyes
Twitter: NaijaEyes
Instagram: NaijaEyes
TikTok: NaijaEyes